The development of a network of skilled Pump Officers aims at providing an immediate and local response to the unforeseen pump breakdowns faced by communities among the district. But it is also a way to allow the communities to enter in a cycle of yearly preventive maintenance of their water supply systems through yearly preventive maintenance campaigns, when they operate a complete diagnosis and a basic maintenance of the systems (cleaning pipes and parts, changing wearing parts…).
These yearly campaigns of maintenance are organised and grouped during one quarter (October, November and December), the best timing for the communities since they get some funds from cropping at this period, increasing their capacity to finance the maintenance. Some weeks before, the assigned Pump Officer visits his communities, with the support of the project at the beginning, to remind them that it is time to do their preventive maintenance and to collect the necessary contributions. This preliminary campaign can be considered as a “promotion tour” while the Pump Officers can make an appointment with the communities for their preventive maintenance. Then, according to the date picked by the community, they operate the yearly maintenance, equipped with the adequate tools and wear parts that are directly purchased by them, in shops pre-identified by Inter Aide.
1/ Identification
The Pump Technicians are selected based on their technical and pedagogical skills as well as how they are perceived by the communities and the Local Authorities (Paramount Chief). Depending on the number of pumps and the accessibility, there are between 1 and 3 Pump Officers per chiefdom.
Other criteria appears essential as well: ability to read and write (mainly for the reporting), behaviour and team spirit, seriousness, conflict management, ability to convince and to sensitize communities, ability for self-promotion, etc.
They are involved throughout all processes of the project in order to familiarise with their job and to progressively become autonomous.
2/ Training & authorities’ certification

HPT under training a woman pump caretaker – evaluation of his pedagogical skills
During 6 months to 1 year, the potential Pump Technicians are involved on all the diagnosis, repairs and maintenances done in their chiefdom under the supervision of Inter Aide. The team plays an active role while developing the skills of the Pump Technicians by gradually involving them in the conduct of the operations, so that they can be ready to do the future preventive maintenances and reparations. It’s a good way to assess their existing knowledge, to train them on the strategy and to reinforce their technical and social skills.
Depending on the number of candidates, the size of the chiefdom and the number of hand pumps to cover, between one and three Pump Officers are finally selected per chiefdom and will attend the training of the Water Supply Division.
For the final selection it is important to not focus only on the technical skills of each candidate. Indeed some others are as much important and more difficult to improve. For instance, the social skills like the way to sensitize, advise and convince a community or the ability to manage a conflict are very useful to develop and run this kind of activity. The behaviour and the team spirit are also some important qualities that must be taken into account.
Once the potential Pump Officers has been identified, another 3 to 4 days training is organised in partnership with the Water Supply Division of Bombali District with representatives of the Ministry of Energy and Water Resources from Freetown.
This training session tackles different aspects of the work as Pump Officers and alternates with theoretical, technical and practical training:
- Presentation of the Pump Officers’ strategy

- Technical training on the different types of hand pumps (based on manuals and guidelines)
- Practical training on hand pumps: presentation of the different spare parts, dismantling/reassembling of a full set of hand pumps with engineers from Freetown, cylinder setting, etc.
- Theoretical and practical training on hand dug well chlorination (guidelines and training on site)
- Theoretical training on social and pedagogical aspects: business management, self promotion, reporting, etc.
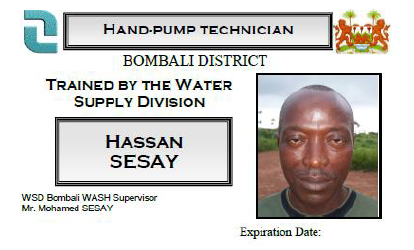
Pump Technician ID card
At the end of this training session each Pump Officer receives his “hand pump technical training certificate” and his ID card. These documents are the proof that the technician is entitled by the government and Inter Aide to work on hand pumps for the well-being of communities. Indeed, it is very important for the Pump Officers to get this certificate, since some communities are quite mistrustful of fake technicians that could steal their pump or replace original parts by fake ones.
The letter in link here is also a document kept by the hand pump technician and has been signed by the Water Directorate and proved his certification : Letter for PO certification by WD
The Pump Officer receives his tool box at the end of the certification training. A money contribution of 25% of the total cost of the box is asked to each Pump Officer (100,000 Le[1] in one shot, balance deducted from the following workmanship). The contract includes a clause to get the tool box back from the Pump Officer in case of breaking-off for any relevant reason.
[1] Approximately 22 USD (1 USD = 4,500 Le)
Agreement for bicycle: to support the Pump Officers for their Promotion tour and the follow up of their communities, Inter Aide proposes to provide a bicycle for a contribution of Le 100,000 (real cost = Le 350,000) in one shot.
3/ Tools used by the HPTs during their actvities
After each interventions, the pump technician is filling a report:
This report, called “Pump Officer declaration of intervention” exists in two different versions depending on the type of pump repaired or maintained: IM2, PB2 and Japanese below or Kardia 65/2000. At the end of each job, the Pump Officers have to fill this report with the secretary of the Water Committee, in the presence of the other members. Two copies have to be filled: one for the community and one for Inter Aide (then photocopied for the WSD and each Pump Officer).
This report has two main purposes. On one hand, it allows the community to keep an update of what has been done on their pump (type of intervention), which part has been replaced and the total cost of the intervention (including chlorination if hand dug well[1]). It also serves as a receipt and a proof of payment, compulsory condition for transparency.
On the other hand, this report is submitted by the Pump Officer to Inter Aide and then to the WSD. The information is immediately recorded in an database. This allows analysing the maintenance activities: status of each pump, number, type and frequency of replaced parts, total cost of each intervention, coverage and respect of preventive maintenance, etc. It is also a good tool to follow the evolution and the progress of each Pump Officer’s activities: potential number of pumps, number of pumps repaired/maintained, generated incomes, etc.
[1] Boreholes are not chlorinated to avoid the corrosion of their casing (most of them have been built with galvanized casing). Moreover, the risk of contamination from outside is reduced with this type of construction.
To help them in their job, Inter Aide developped simplified hand pump maintenance guidelines that they can keep as a reminder (a summary of the complete ones) + guidelines for well chlorination:
They have, as water committees, hand-pump price lists that enable them to quote their intervention :
4/ Promotion of their services
In order to increase their visibility among the communities, apart from the sensitization Inter Aide is doing toward water committees, some promotional means are used such as:
- stickers that are displayed near the water point

- promotional flyers

 Results of the initial survey made end of 2010 in Sierra Leone for the districts of Bo, Koinadugu andTonkolili on 2’854 water points regarding the status of the infrastructures. This study is a detailed analyze of the current conditions of wells and boreholes equiped with hand pumps in rural areas of Sierra Leone.
Results of the initial survey made end of 2010 in Sierra Leone for the districts of Bo, Koinadugu andTonkolili on 2’854 water points regarding the status of the infrastructures. This study is a detailed analyze of the current conditions of wells and boreholes equiped with hand pumps in rural areas of Sierra Leone.











 The short note in link gives some key elements on the following questions: What is the cost of maintaining a pump in rural areas? How much does it represent per family user? Is it affordable? How can these contributions be organised and managed at village level?
The short note in link gives some key elements on the following questions: What is the cost of maintaining a pump in rural areas? How much does it represent per family user? Is it affordable? How can these contributions be organised and managed at village level?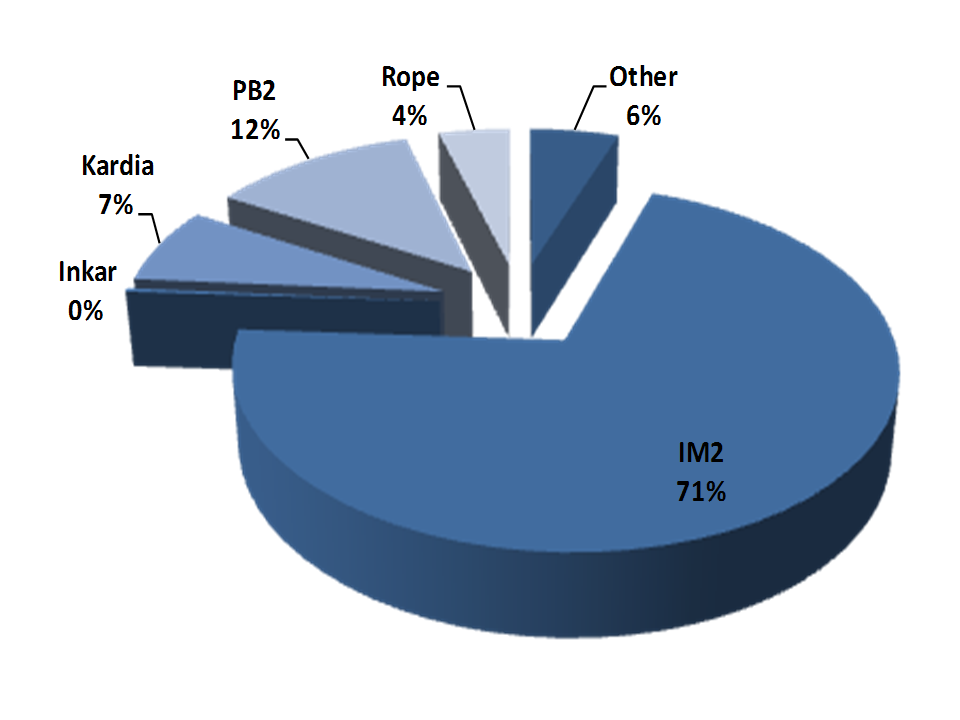
 Hand pump made in India: galvanized or stainless type. In Sierra Leone, this pump is available in most of the suppliers at a reasonable cost for stainless type (around 2.900.000 SLL) and offers a good quality for its price. A regular maintenance is compulsory to ensure the sustainability and avoid major breakdown. The installation process is also really important and has to be done properly (iron rods lengths, cylinder position from the bottom, hand pump stand straight…).
Hand pump made in India: galvanized or stainless type. In Sierra Leone, this pump is available in most of the suppliers at a reasonable cost for stainless type (around 2.900.000 SLL) and offers a good quality for its price. A regular maintenance is compulsory to ensure the sustainability and avoid major breakdown. The installation process is also really important and has to be done properly (iron rods lengths, cylinder position from the bottom, hand pump stand straight…).