| Inter Aide | Contact |
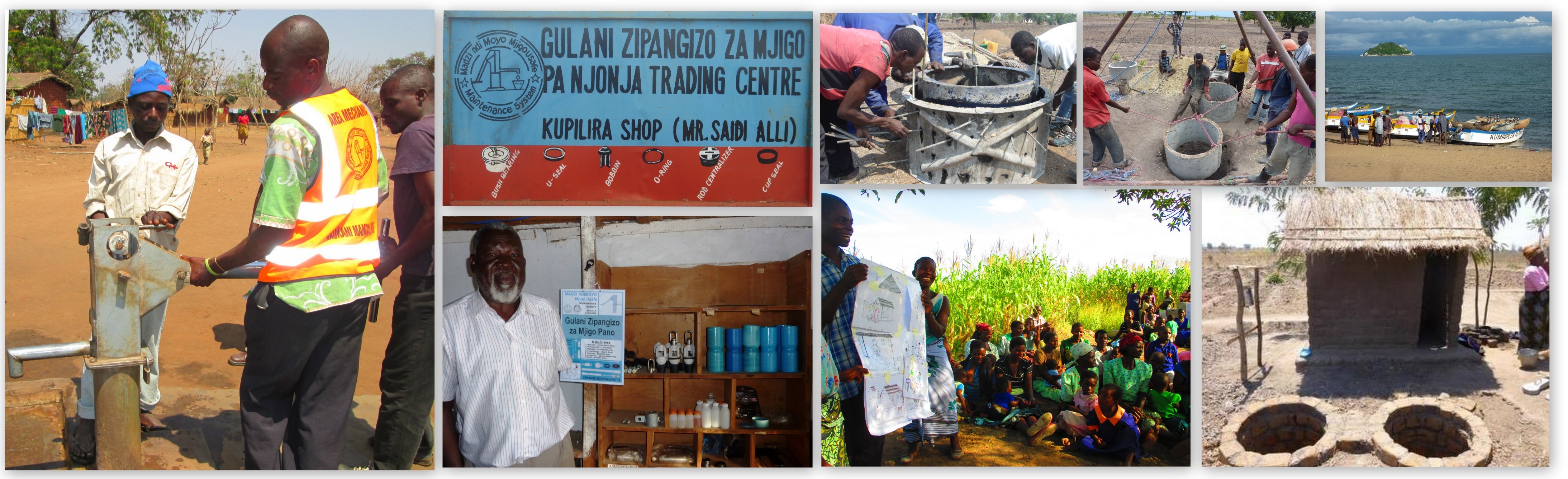


It can be any shop which is clearly identified by the communities, frequented, which is well located in a trading center and for which his owner is ready to support the communities by facilitating access to hand pump spare parts.
Generally it can be hardware shops, groceries, even tailors…
They agree to collaborate with Inter Aide, BASEDA, TIMMS, and since 2012 with RUWASO who are linking them with main suppliers of Afridev and Malda pumps located in main cities like Lilongwe and Blantyre, and they are reselling (with some profit – around 20% for the fast wearing parts) to any water point users, thus facilitating access even for remote villages.

M. Guande, shop owner, in front of the shelf that displays the spare parts to the customers
Shops owners are selected also according to their capacities to manage and develop such business. Selection is made with the advises of District Councils and Water Departments.
Then, they are trained to have the basic knowledge of the use of spare parts, bust most of all to well manage this activity so that water point users are well oriented and can always find the parts they are looking for.

Sign boards used to identify spare parts resellers
In 2016, there are 150 spare parts retailers in Malawi who have been trained by Inter Aide – BASEDA – TIMMS, see details on the map.
The complete list of partners shops (and AMs) for 2016 is available here: BROCHURE List of all AM SHOPS
 List all related tools for the identification, training, follow-up of Area Mechanics.
List all related tools for the identification, training, follow-up of Area Mechanics.
Selection / recruitment
Trainings
Operation
| Visibility | |
|
|
Monitoring & Evaluation
| Quantitative | Qualitative |
Complete catalog:
www.interaide.org/watsan/malawi/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/AM-network-catalog.pdf
1 District Councils
The Council is supposed to be headed by the Chairperson selected from amongst its 10 councilors each representing a ward in the district. The District Commissioner is the head of Council Secretariat, which is composed of Professional Heads of Government Sectors in the district.
The council must have the following service committees: Finance Committee; Development Committee; Education Committee; Works Committee, Appointment and Disciplinary Committee Health and Environment Committee which is the custodian committee on water and sanitation issues. It may establish other committees when need arises.
2 District Executive Committee – DEC
This is a technical body that provides advice to the Council and its service committees. It is composed of all Heads of Departments and NGO/Development partners in the district. The District Executive has a membership of 50, chaired by the District Commissioner while the Director of Planning and Development is its secretary. The DEC has a subcommittee of District Coordinating Team (DCT) on water, sanitation and hygiene. Membership of the committee consists of both the sector heads and non-state actors involved in water, sanitation and hygiene. The committee is chaired by the Director of Planning and Development with secretariat for sanitation in Health Sector. The main role of the DCT is coordination of water, sanitation and hygiene activities in the district.
3 Area Development Committees – ADCs
The Area Development Committee (ADC) is a representative body of all Village Development Committees under a Traditional Authority. Its membership could range from 25 to 60 under the patronage of the Chief. It mobilizes community resources and implements development interventions within it’s the area.
Membership includes Group Village Headpersons, Representative of Women Groups, and representative of Youth Groups, the District Councilors of the area, and Business and Religious Leaders. The district follows a decentralized approach in implementing all projects in the district, water and sanitation inclusive. It is the role of the ADC to prioritize the demand driven WASH projects from all village development committee’s in a traditional authority.
The ADC also assists in the identification an overall project that cuts across the ADC i.e. piped water systems and mobilization of resources during the course of implementation of a project.
4 Area Executive Committees – AECs
An Area Executive Committee is composed of Extension workers of Government and Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) operating in the Traditional Area. At the area level Government extension workers in the WASH sector are the Health surveillance assistance and water monitoring assistant. This committee is the technical arm at the area level responsible for advising the ADCs on all aspects of development.
5 Village Development Committees – VDCs
This is a representative body from a group of villages responsible for identifying needs and facilitating planning and development in local communities. It is at this level that the communities raise their needs and demand projects like boreholes or taps. The VDC is chaired by an elected chair which the group village head is patron. Members of the VDC include members of the following committees and groups:
At national level, the Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Water development is responsible for water supply and sanitation services[1], and is itself divided into different Departments:
The Water Supply and Sanitation Department oversees formulation of sector policies, sets technical standards and procedures for the provision of services; plans, designs the construction of water supply schemes; and trains communities in proper management of water supply schemes.[2]
At district level, The Water Department headed by the District Water Officer is the entity giving the direction and strategies for development of water access. It is evaluating where the needs and the priorities are, deciding of new infrastructures.
WMAs (Water Monitoring Assistants) are in charge to train and monitor Water Point Committees. Inter Aide, BASEDA and TIMMS are collaborating with them for the supervision of the activities of Area Mechanics (the idea is to progressively organize a transfer of competencies).
BMOs (Borehole Maintenance Overseer) – a position which does not exist in all districts – are in charge of managing construction of boreholes and major rehabilitation. They are also supervising and giving support to campaigns leaded by other operators (NGOs…). They can advise Area Mechanics for the repairs.
![]()
The Area Development Committee – ADC and traditional authorities are asked to do a pre-selection of persons who could be potential AMs with recommendations from District Water Officer. This pre-selection have to take into considerations where the needs are, i.e. where the persons would have to be located to tackle a catchment with an important but manageable density of hand pumps (more than 100 hand pumps is difficult), considering also the radius of activity and topography-accessibility.
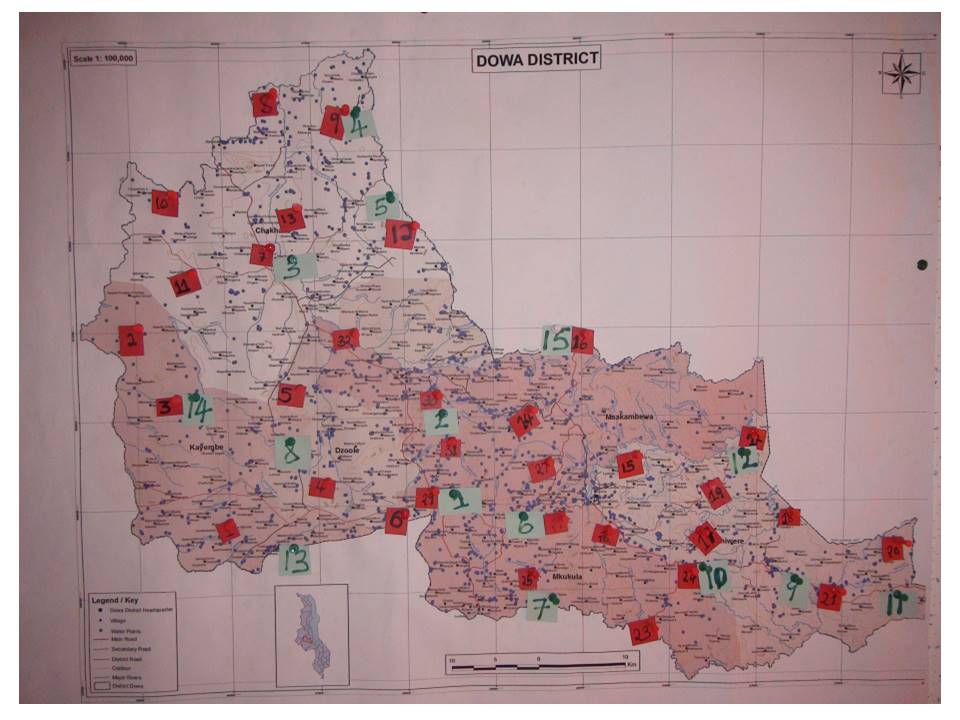
The example of this Map of Dowa district illustrates the brainstorming done for the distribution of AMs (red stickers) and shops (green labels)
Oral interviews are conducted jointly with DWO, the ADC chairman, and Health Surveillance Assistant HAS (15 to 20 min. per candidate).
Criteria of selection include technical knowledge, but also abilities to communicate with water points’ users, dedication for development and helping the community, capable of reading, writing, counting, willingness to develop such business…Some written tests are also conducted.
Links :
BASEDA guidelines interview AM interview form![]()
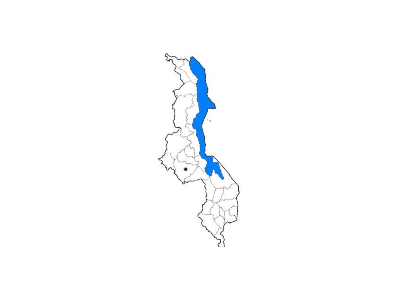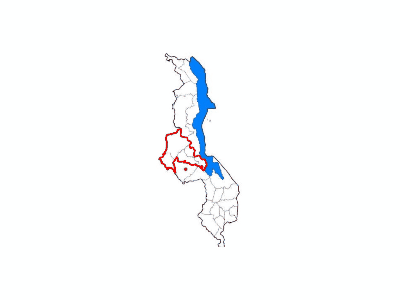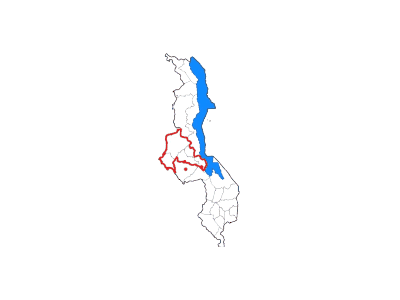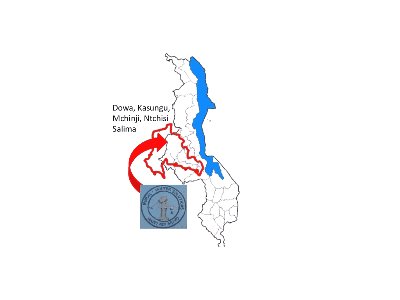
RUral WAter SOlutions is a Malawian social entrepreneurship company founded in 2013 aiming at providing a reliable supply chain for Afridev and Malda hand pumps spare parts. Operating in 5 districts (Dowa, Kasungu, Mchinji, Ntchisi and Salima), RUWASO rely on 60 partner shop owners in the trading centers of rural areas.
See more details on the complete description document below: company profile working document ![]()
Before 2013, the supply of the spare parts retailers was provided by Inter Aide who was buying in bulk to main suppliers in Lilongwe or Blantyre. With the creation of RUWASO, a local solution has been set up, which should be more sustainable.
RUWASO is relying on the public transport to distribute the items and link its central depots with suppliers and retailers.
The supply of these 5 districts is completely autonomous and RUWASO is able to make some profit and to pay its staff, the rent of the depot and all materials required.
Area Mechanics training are done through a participatory approach with 80% dedicated to practical and real field situations. The initial training deals with 2 VLOM pumps as designated by the Malawi Government namely, Afridev and MALDA hand pumps.
Demand generated refresher trainings are organized to update AM skills in pump repairs. We organize quarterly review meetings to offer AMs an opportunity to share technical challenges and field experiences providing additional ways in improving AMs’ skills.
Links :